| [1] Melrose J. Strategies in regenerative medicine for intervertebral disc repair using mesenchymal stem cells and bioscaffolds. Regen Med. 2016;11(7):705-724.[2] Stubbs B,Koyanagi A,Thompson T,et al. The epidemiology of back pain and its relationship with depression, psychosis, anxiety, sleep disturbances, and stress sensitivity: Data from 43 low- and middle-income countries. Gen Hosp Psychiatry.2016;43:63-70.[3] Shmagel A, Foley Rand Ibrahim H. Epidemiology of Chronic Low Back Pain in US Adults: Data From the 2009-2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016;68(11):1688-1694.[4] Cheung KM,Karppinen J,Chan D, et al.Prevalence and pattern of lumbar magnetic resonance imaging changes in a population study of one thousand forty-three individuals. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(9):934-940.[5] Takatalo J,Karppinen J,Niinimaki J,et al. Does Lumbar Disc Degeneration on Magnetic Resonance Imaging Associate With Low Back Symptom Severity in Young Finnish Adults?.Spine.2011; 36(25):2180-2189.[6] Dario AB,Ferreira ML,Refshauge KM,et al.The relationship between obesity, low back pain, and lumbar disc degeneration when genetics and the environment are considered: a systematic review of twin studies.Spine J.2015;15(5):1106-1117.[7] Battie MC,Videman T. Lumbar disc degeneration: Epidemiology and genetics. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2:3-9. [8] Tarnoki AD,Tarnoki DL,Kovacs DT,et al.Genetic relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and lumbar disc degeneration: results from a twin study. European Respiratory Journal. 2017; 50.[9] Zhou X,Cheung CL,Karasugi T,et al.Trans-Ethnic Polygenic Analysis Supports Genetic Overlaps of Lumbar Disc Degeneration With Height, Body Mass Index, and Bone Mineral Density. Front Genet. 2018;9:267.[10] Battie MC, Videman Tand Parent E. Lumbar disc degeneration - Epidemiology and genetic influences. Spine.2004;29(23): 2679-2690.[11] Bjornsdottir G, Benonisdottir S, Sveinbjornsson G, et al. Sequence variant at 8q24.21 associates with sciatica caused by lumbar disc herniation. Nature Communications.2017, 8.[12] Baldwin Aand Mesfin A. Adjacent Segment Disease 44 Years Following Posterior Spinal Fusion for Congenital Lumbar Kyphosis. Spine Deform.2017;5(6):435-439.[13] Dong L,Xu Z,Chen X,et al.The change of adjacent segment after cervical disc arthroplasty compared with anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Spine J.2017;17(10):1549-1558.[14] Arnbak B,Jensen RK,Manniche C,et al.Identification of subgroups of inflammatory and degenerative MRI findings in the spine and sacroiliac joints: a latent class analysis of 1037 patients with persistent low back pain.Arthritis Res Ther.2016;18(1):237.[15] Muriuki MG, Havey RM,Voronov LI,et al. Effects of motion segment level, Pfirrmann intervertebral disc degeneration grade and gender on lumbar spine kinematics.J Orthop Res.2016; 34(8):1389-1398.[16] Xiao L,Ni CL,Shi JD,et al.Analysis of Correlation Between Vertebral Endplate Change and Lumbar Disc Degeneration. Medical Science Monitor.2017;23:4932-4938.[17] Wu B,Meng C,Wang H,et al.Changes of proteoglycan and collagen II of the adjacent intervertebral disc in the cervical instability models. Biomed Pharmacother.2016; 84:754-758.[18] Grant MP,Epure LM,Bokhari R,et al.Human cartilaginous endplate degeneration is induced by calcium and the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in the intervertebral disc. Eur Cell Mater. 2016;32:137-151.[19] Xu HG,Zheng Q,Song JX,et al.Intermittent cyclic mechanical tension promotes endplate cartilage degeneration via canonical Wnt signaling pathway and E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex cross-talk. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(1):158-168.[20] Sivan SS, Hayes AJ, Wachtel E, et al. Biochemical composition and turnover of the extracellular matrix of the normal and degenerate intervertebral disc. Eur Spine J.2014;23 Suppl 3: S344-53.[21] Garnero P. The Role of Collagen Organization on the Properties of Bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015,97(3):229-240.[22] 张学利,宋海峰,朱如森,等.Ⅸ型胶原蛋白A2基因多态性与环境因素在腰椎间盘退变疾病中的作用[J] 中华实验外科杂志,2017, 34(7): 1232-1235.[23] Wu HH, Wang ST, Chen WY, et al. Collagen IX gene polymorphisms and lumbar disc degeneration: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):47.[24] Mio F, Chiba K, Hirose Y, et al. A functional polymorphism in COL11A1, which encodes the alpha 1 chain of type XI collagen, is associated with susceptibility to lumbar disc herniation[J]. Am J Hum Genet.2007;81(6):1271-1277.[25] Ruel N, Markova DZ,Adams SL,et al.Fibronectin fragments and the cleaving enzyme ADAM-8 in the degenerative human intervertebral disc.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2014; 39(16):1274-1279.[26] Urano T,Narusawa K,Shiraki M,et al.Single-nucleotide polymorphism in the hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1 (HAPLN1) gene is associated with spinal osteophyte formation and disc degeneration in Japanese women. Eur Spine J.2011; 20(4):572-577.[27] S M H, M K S, G K C, et al. Association of CILP, COL9A2 and MMP3 Gene Polymorphisms with Lumbar Disc Degeneration in an Indian Population.J Mol Neurosci.2018;66(3):378-382.[28] Li Y, Li K, Han XG, et al. The imbalance between TIMP3 and matrix-degrading enzymes plays an important role in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2016, 469(3):507-514.[29] 张博,杨少华,林世洲,等.基质金属蛋白酶1在不同程度退变腰椎间盘髓核与纤维环中的表达及意义 [J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(13): 2346-2349.[30] Deng B, Ren JZ, Meng XQ, et al. Expression profiles of MMP-1 and TIMP-1 in lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Genet Mol Res.2015;14(4):19080-19086.[31] Yuan HY, Tang Y, Lei L, et al.[Synergistic interaction between MMP-3, VDR gene polymorphisms and occupational risk factors on lumbar disc degeneration]. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi.2010;28(5):334-338.[32] Williams FMK, Bansal AT, van Meurs JB, et al. Novel genetic variants associated with lumbar disc degeneration in northern Europeans: a meta-analysis of 4600 subjects. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2013, 72(7):1141-1148.[33] Lin WP,Lin JH,Chen XW,et al.Interleukin-10 promoter polymorphisms associated with susceptibility to lumbar disc degeneration in a Chinese cohort.Genet Mol Res.2011;10(3): 1719-1727.[34] Omair A,Lie BA,Reikeras O, et al. An Association Study of Interleukin 18 Receptor Genes (IL18R1 and IL18RAP) in Lumbar Disc Degeneration. Open Orthop J.2012; 6:164-171.[35] Jiang H, Qin Z,Zong S,et al. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and lumbar disc degeneration: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J.2017;26(1):267-277.[36] Zawilla NH, Darweesh H, Mansour N,et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-3, vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms, and occupational risk factors in lumbar disc degeneration. J Occup Rehabil.2014; 24(2):370-381.[37] Yuan HY,Tang Y,Liang YX,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase-3 and vitamin d receptor genetic polymorphisms, and their interactions with occupational exposure in lumbar disc degeneration. J Occup Health.2010;52(1):23-30.[38] Schultz DR,Harrington WJ Jr.. Apoptosis: Programmed cell death at a molecular level. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2003;32(6):345-369.[39] Ariga K,Yonenobu K,Nakase T,et al.Mechanical stress-induced apoptosis of endplate chondrocytes in organ-cultured mouse intervertebral discs - An ex vivo study.Spine.2003; 28(14): 1528-1533.[40] Sakai D, Nakamura Y, Nakai T, et al. Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Nat Commun.2012;3:1264.[41] Jiang M, Zhu K, Grenet J, et al.Retinoic acid induces caspase-8 transcription via phospho-CREB and increases apoptotic responses to death stimuli in neuroblastoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1783(6):1055-1067.[42] Wang X, Luo T, Ruan M, et al. Association of the CCDC26 rs4295627 polymorphism with the risk of glioma: Evidence from 7,290 cases and 11,630 controls. Mol Clin Oncol.2016;4(5): 878-882.[43] Cao K, Li M, Miao J, et al. CCDC26 knockdown enhances resistance of gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells to imatinib by interacting with c-KIT.Am J Transl Res.2018;10(1):274-282.[44] Zeng J, Luo Y, Yu M, et al.CCDC26 rs4295627 polymorphisms associated with an increased risk of glioma: A meta-analysis. Adv Clin Exp Med.2017; 26(8):1275-1281.[45] Peng Wand Jiang A.Long noncoding RNA CCDC26 as a potential predictor biomarker contributes to tumorigenesis in pancreatic cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.2016;83:712-717.[46] Wang SL, Hui YZ, Li XM, et al. Silencing of lncRNA CCDC26 Restrains the Growth and Migration of Glioma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo via Targeting miR-203.Oncology Res.2018; 26(8):1143-1154.[47] Izadifard M, Pashaiefar H, Yaghmaie M, et al. Expression Analysis of PVT1, CCDC26, and CCAT1 Long Noncoding RNAs in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2018;22(10):593-598. [48] Vaubel R,Kollmeyer T,Caron A,et al.Synchronous gemistocytic astrocytoma IDH-mutant and oligodendroglioma IDH-mutant and 1p19q-codeleted in a patient with CCDC26 polymorphism. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;134(2):317-319. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
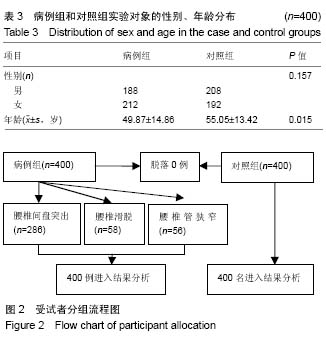
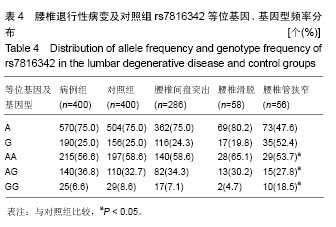
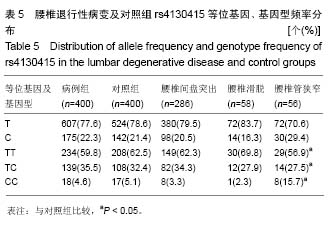
.jpg)
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
单核苷酸多态性:指由于单个核苷酸碱基改变而导致核酸序列的多态性。不同个体的同一条染色体或同一位点的核苷酸序列中,绝大多数核苷酸序列一致而只有一个碱基不同的现象。人群中任意2个不相关的个体DNA序列有99.8%是相同的,而余下的0.2%包含了遗传上的差异因素,造成了不同的生理表型,罹患疾病的风险等。#br#
全基因组关联分析:指人类全基因组范围内找出存在的序列变异,即从中筛选出与疾病相关的单核苷酸多态性位点。在很多捕获了整个基因组的大部分遗传信息单核苷酸多态性中,检测与疾病或者性状的联系的单核苷酸多态性位点,全基因组关联分析可以识别与疾病和性状风险直接或者间接相关的变异。#br#
#br#
#br#
文题释义:#br#
单核苷酸多态性:指由于单个核苷酸碱基改变而导致核酸序列的多态性。不同个体的同一条染色体或同一位点的核苷酸序列中,绝大多数核苷酸序列一致而只有一个碱基不同的现象。人群中任意2个不相关的个体DNA序列有99.8%是相同的,而余下的0.2%包含了遗传上的差异因素,造成了不同的生理表型,罹患疾病的风险等。#br#
全基因组关联分析:指人类全基因组范围内找出存在的序列变异,即从中筛选出与疾病相关的单核苷酸多态性位点。在很多捕获了整个基因组的大部分遗传信息单核苷酸多态性中,检测与疾病或者性状的联系的单核苷酸多态性位点,全基因组关联分析可以识别与疾病和性状风险直接或者间接相关的变异。#br#
#br#